What is Linear Measurement?| What are the linear measurement instruments?
In Metrology Linear measurement applies to the measurement of lengths, diameters, heights and thickness including external and internal measurements.
Instruments used for Linear Measurement:
Linear measurement instruments can be classified into Direct and indirect measuring instruments.
- Direct measuring instruments.
- Graduated Measuring instruments
- Non Graduated measuring instruments
- Indirect measuring instruments.
They can be further classified into Precision and Non-Precision gauges.
The graduated Instruments:
Rules:
The most common instrument for measurement is scale. It can be made up of Plastic, wood. Tempered Steel alloys can also be used as materials for precision scales. This is Non-precise measurement gauge.

Pierre Vernier Caliper
-------------------------------
This is a precise measuring instrument, Comparatively low accuracy than the other precision measuring instruments. The different types Vernier calipers are available to measure internal, external measurements. See the following Fig:
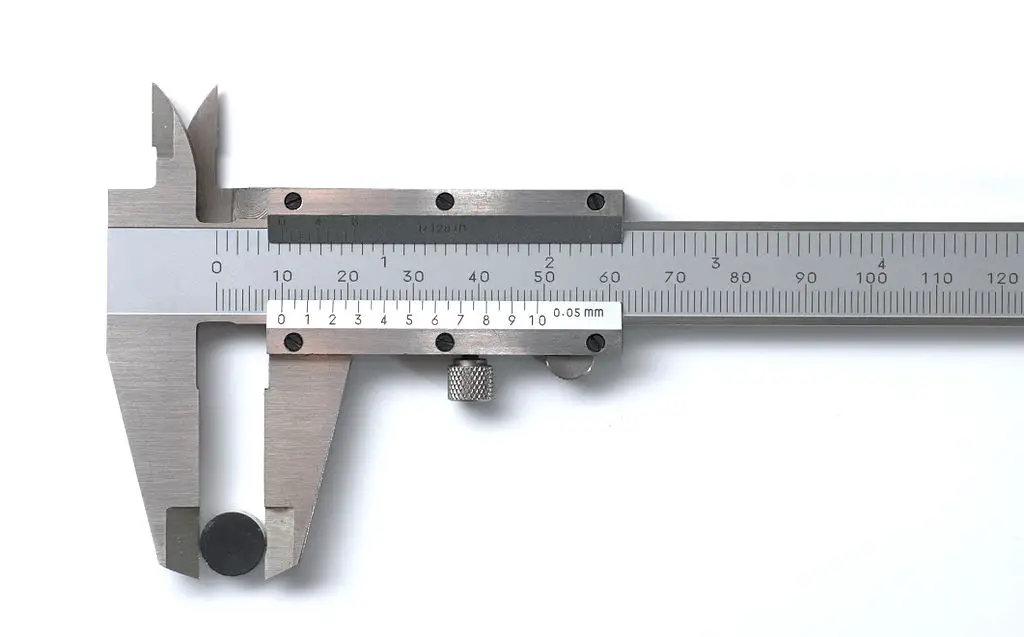

Vernier calliper consists of two scales. One is fixed and the other is movable. The fixed scale is called the main scale. It is a calibrated L-shape frame and carries a fixed jaw. the movable scale, called Vernier scale. Which is slides over the main scale and carries movable jaw. these movable and fixed jaws having to measure tips for internal and external measurements.
Vernier Height Gauge
----------------------------
It is used to determine the height of the objects. The vernier Height gauge measures the object height by using the underside of the scriber as the datum. This datum may be permanently fixed or height gauge will have the provision to adjust the scale. see the below picture:

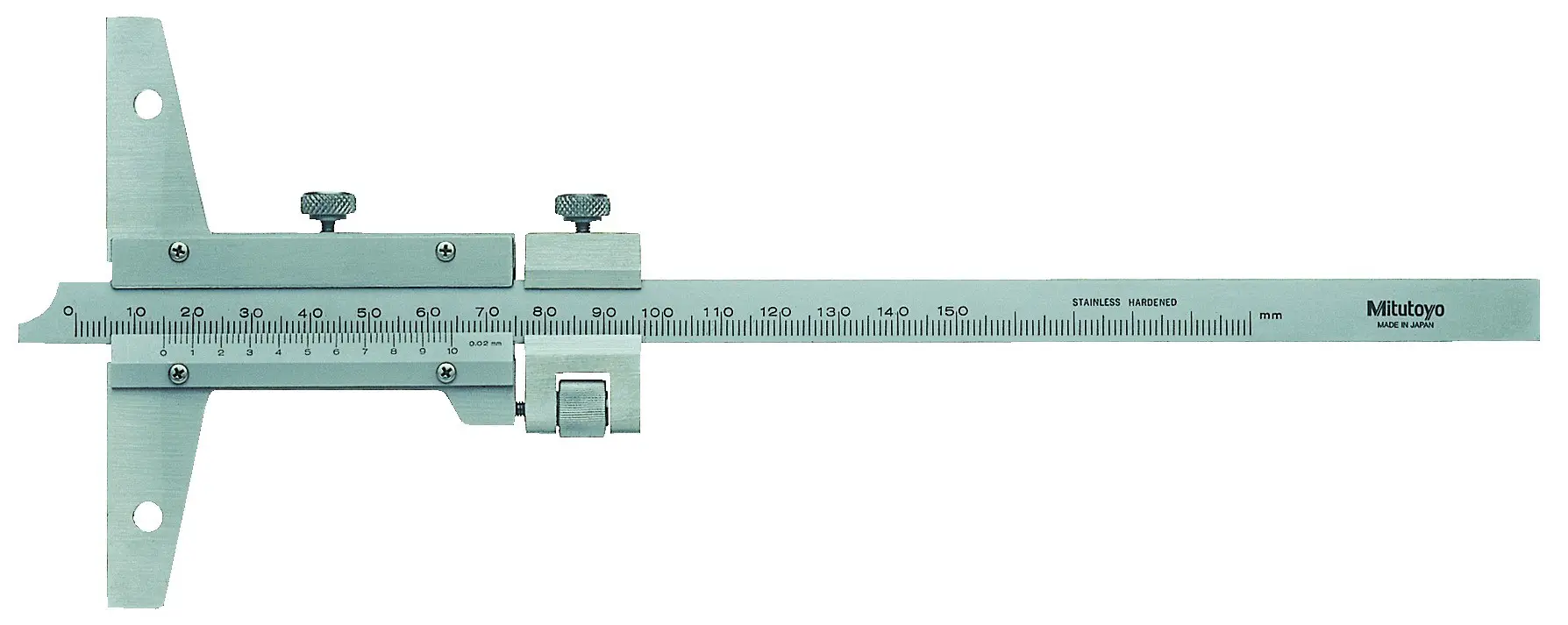
Vernier Depth Gauge
------------------------------------
Vernier depth gauge can be used to measure the depth of the holes. Here we can use extension rods if necessary. See the following picture.
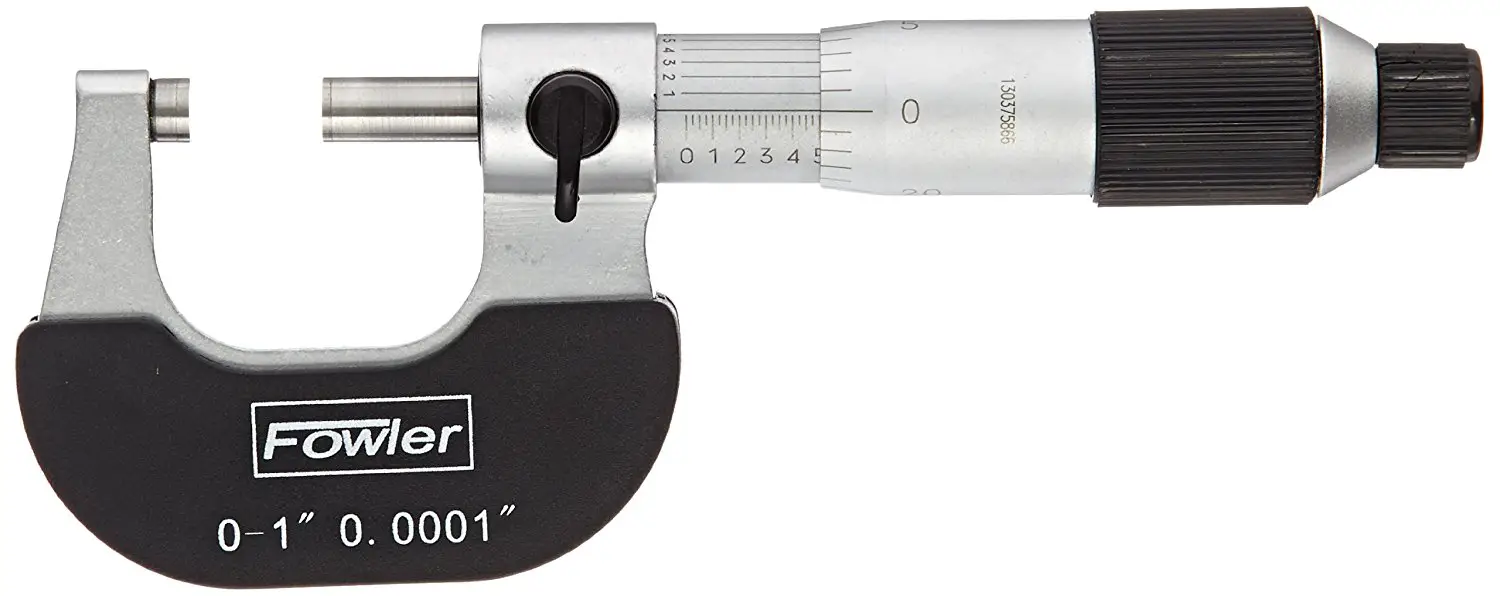
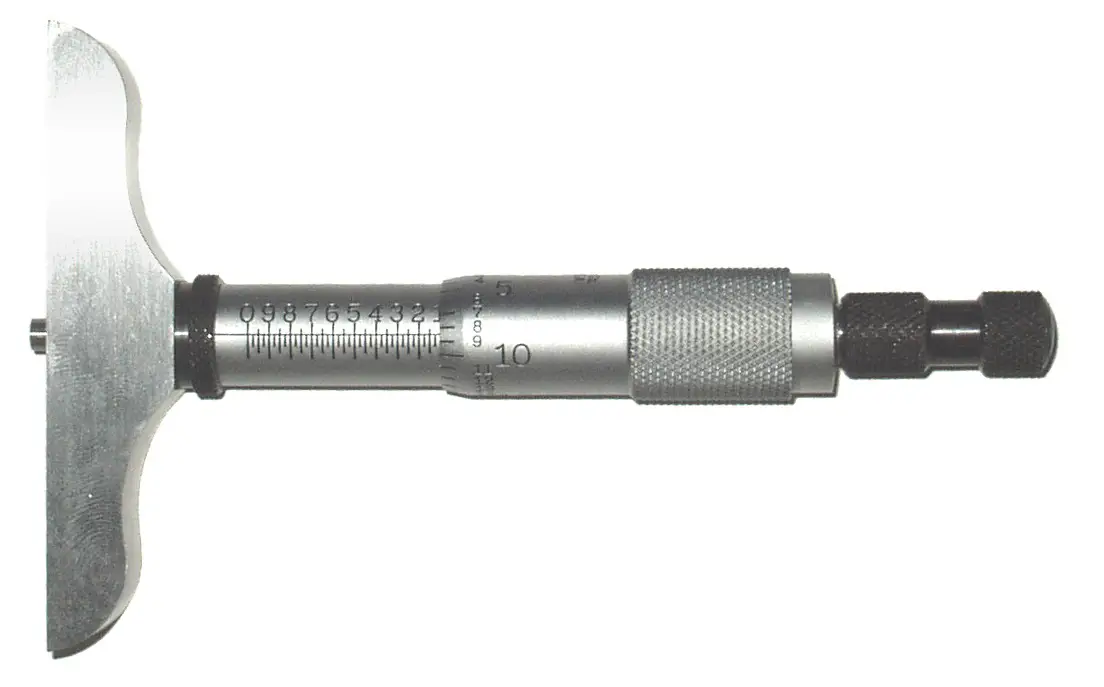
Micrometer
--------------------
Also known as because a calibrated screw is used for precise measurements in this instruments. We can measure the inside, outside diameters, depths as well. This is also used in microscopes to measure the microscopic objects. See the different Micrometers available for measuring internal, external, deep measurements



Dial Indicators
-------------------------------------
used measure the small distances, angles. It is widely used in checking the tolerances during the inspection of the machined component and deflection of the beams.

Non-graduated Instruments:
Caliper
Caliper is used to measure the diameters of the circular parts. The calliper consists two legs hinged at the top. These legs are made of carbon and alloy steels.
There are two callipers(Outside, Inside Callipers)
A. Fixed Joint Calliper (Left: Outside, Right: Inside)
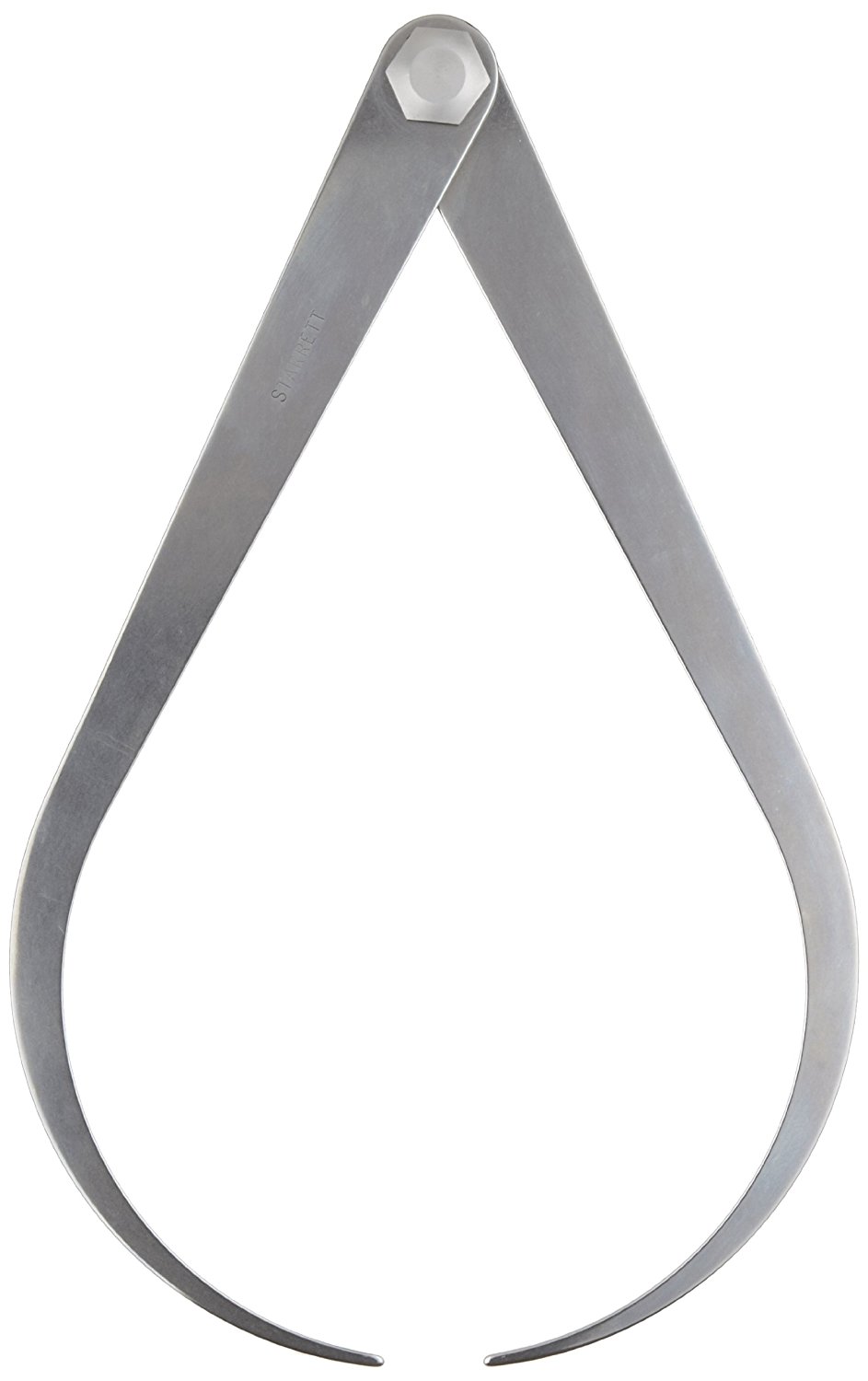


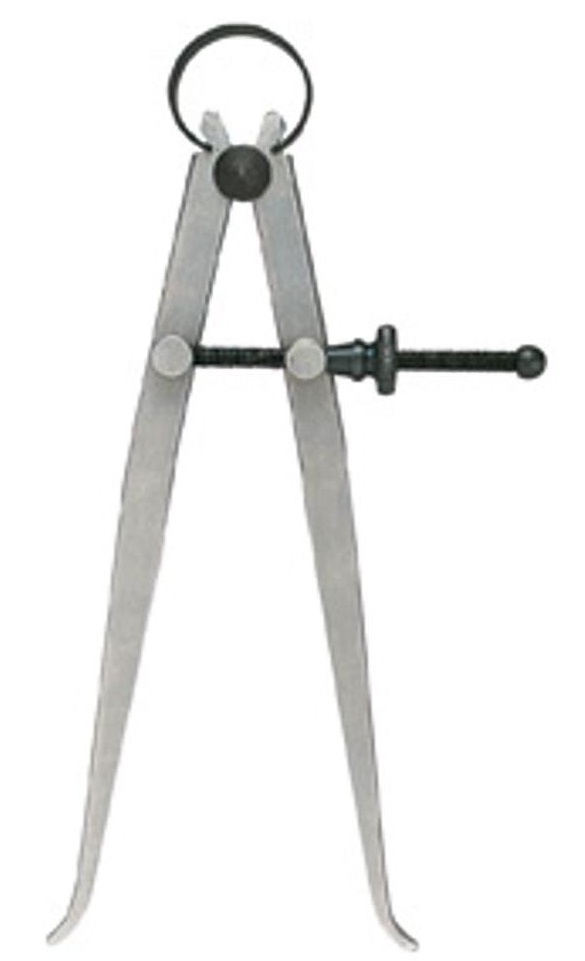
B. Spring type Caliper (Left: Outside, Right: Inside)


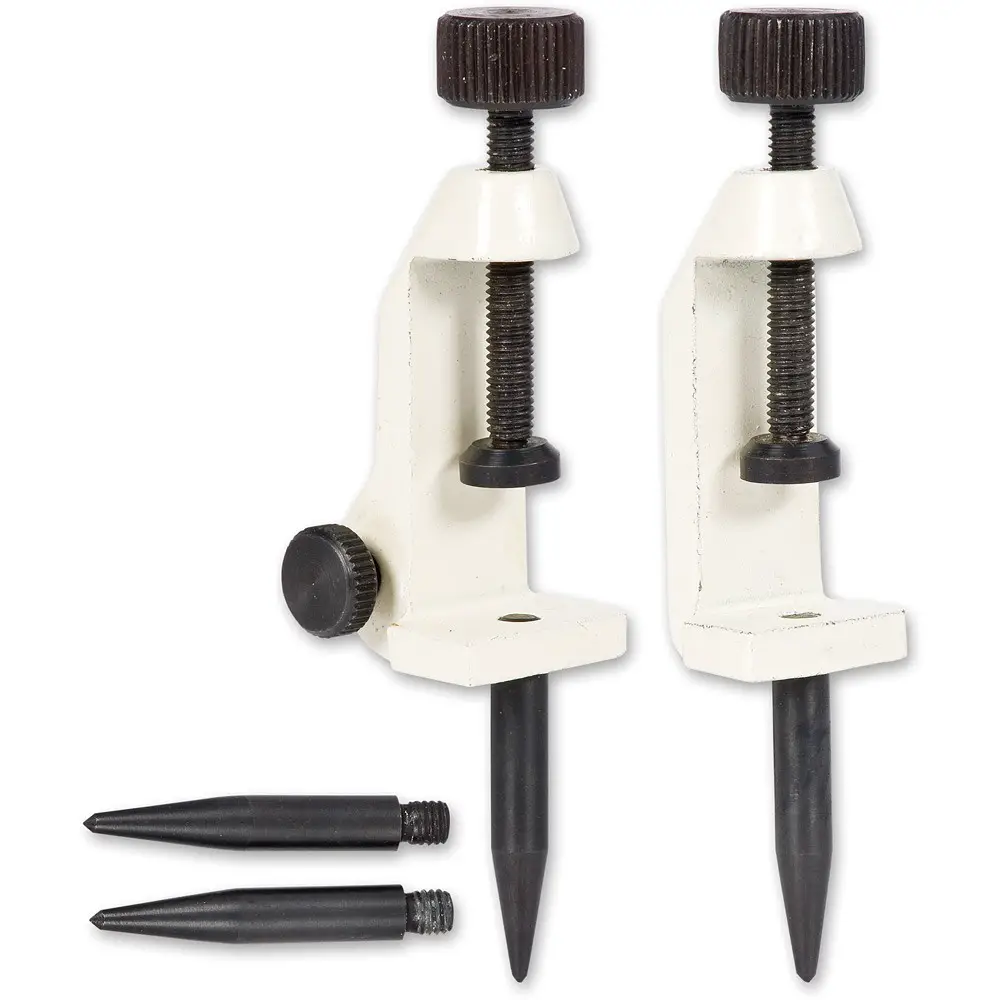
Trammel (Trammels heads)
Trammel’s heads are Clamped onto a rectangular bar for scribing arc’s and circles, marking out sheet work. See the following Images.


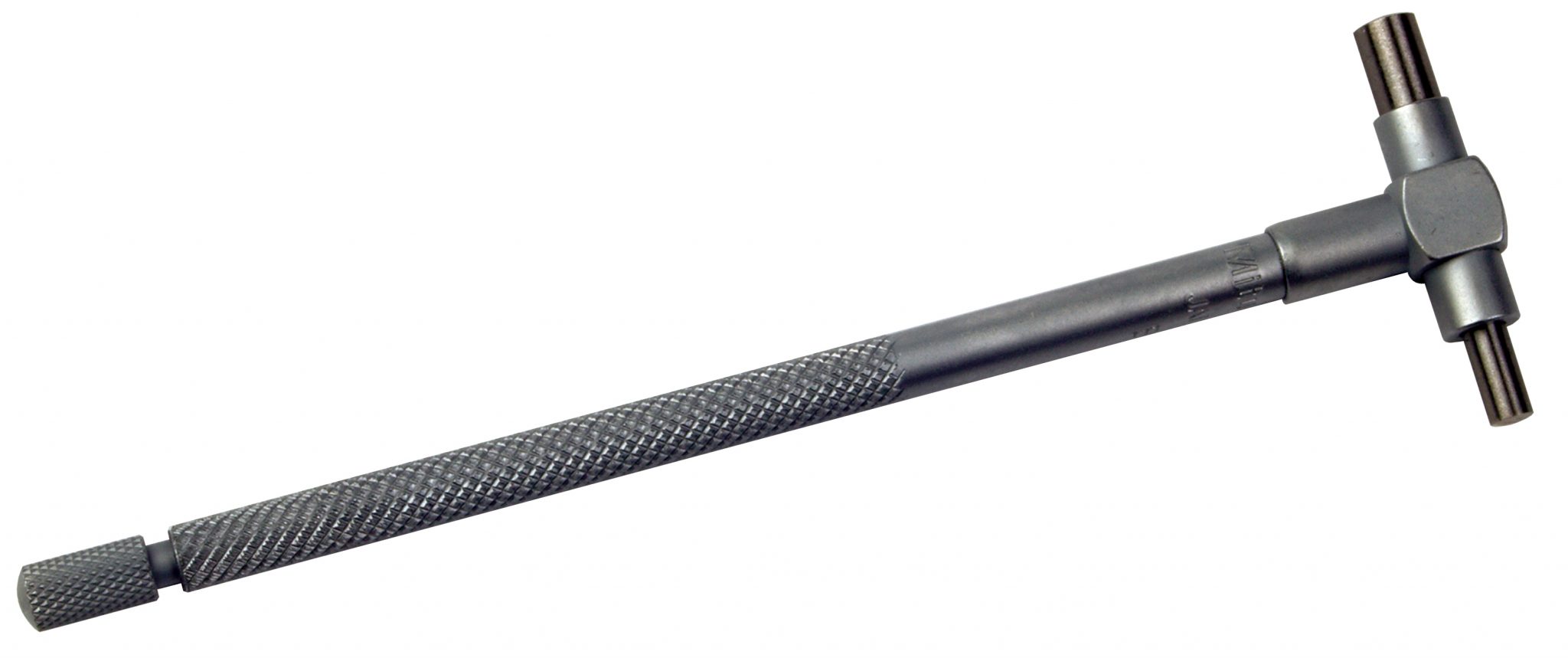
Telescope gauges
This is used to measure diameters of holes or bores. This instrument having spring-loaded plunges used together with a micrometre and has a handle that is attached to two spring-loaded plungers. It can measure small to very large bores.

Surface Gauges
Used to find the centre of round section material. It is used to scribe parallel lines. This surface gauge will have a magnetic base so that they can lock to the position. Mostly this surface gauge is used along with the V-Block. the cylindrical object will be placed on the V-Block to mark the parallel lines on the Object.

Straight Edges
Straight edges are used for drawing straight lines or checking their straightness.
If it has equally spaced markings along its length, it is usually called a Ruler
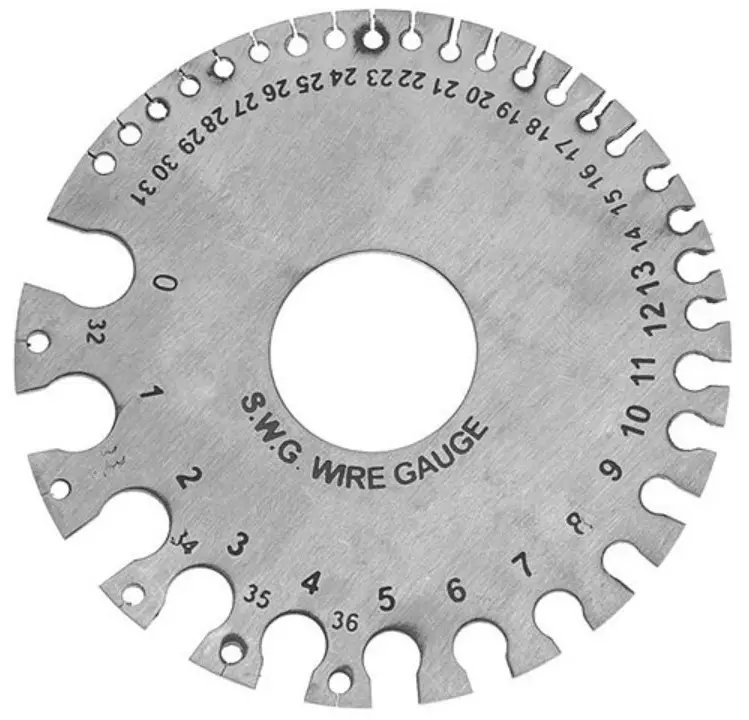
Wire Gauges
Wire gauge is used to measure the diameters of the wires. These wire gauges are in circular or oblong shape and it is having notches along the edges of the shape(as shown in below picture) and each notch is stamped with wire size number.

Screw Pitch Guages
Also known as Thread Gauge Or Pitch Gauge used to measure the pitch or lead of the screw thread. Screw pitch gauges are not used in precision measurements rather it allows the user to determine the profile of the given thread. We can quickly categorize the thread by shape and pitch of the screw thread by using the Pitch Gauge.

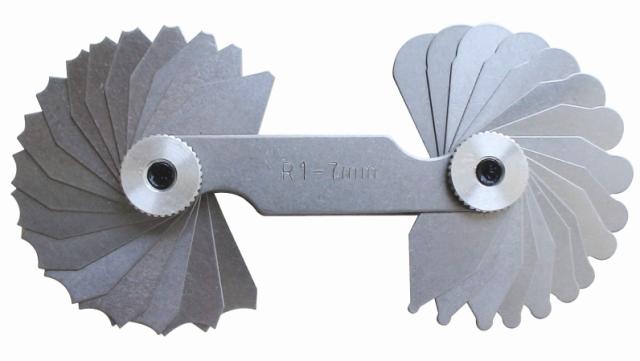
Radius Gauges
Also known as Fillet Gauge. Radius gauge is used to measure the radius of the object. These are also not used in precision measurements rather it allows the user to quickly determine the fillet radius.
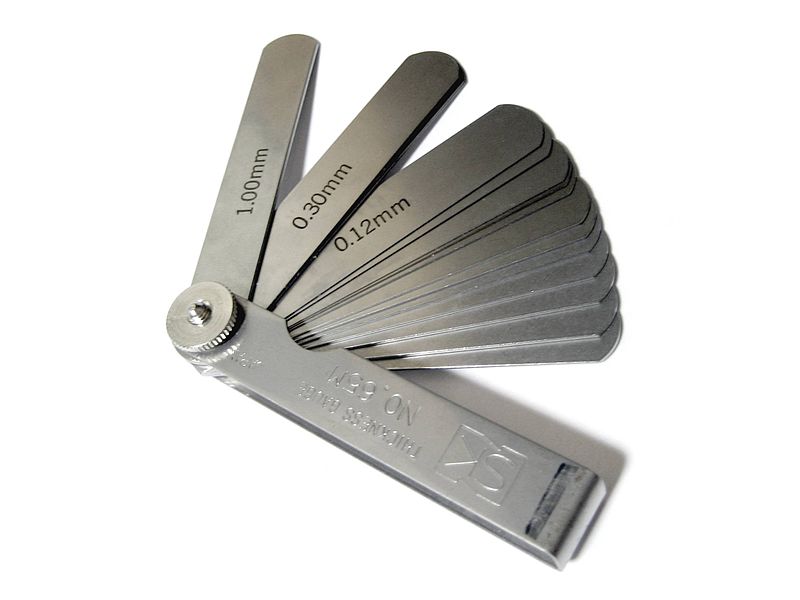
Thickness Gauges
Used to measure the thickness of the objects(Sheet metal). Thickness gauge will have a stack of different thickness sheets and stamped with the thickness size. Thickness gauges are not used in precision measurements rather it allows the user to quickly determine the thickness of the sheets.

Slip Gauges

These have come with a set of a box. The individual block is precision ground and lapped specific thickness. These blocks are stacked together to make up the desired length. See the below Example
Example
These are the Different instruments available in metrology for linear measurement.
Comments
Post a Comment